Edge Computing is transforming operations across industries from food & beverage to oil & gas, as well as commercial building management. This emergent technology harnesses real-time data from critical equipment and processes to dramatically improve operational efficiency and enable new insights through advanced analytics.
These capabilities act as a foundation for smart cities, smart infrastructure, and Industry 4.0 manufacturing. By leveraging connectivity, collaboration, and insight, smart applications create business value, increase competitive advantage, and enhance productivity.
Given the impact that Edge Computing is having, it’s only natural for the next question to be, “What does Edge Computing mean in practical terms for control engineers, IT infrastructure and operations leads, building managers, and other leaders?”
What is Edge Computing? A pragmatic definition
Edge Computing is a distributed computing model in which computing takes place at the edge of operations – where data is generated – aggregating, processing, and analyzing this data at the edge, rather than on a centralized server or in the cloud. Edge Computing builds a bridge between real-time data acquisition from mission-critical processes to the control room, cloud, or operations center, providing local compute capability at edge locations – or the operational edge – for shop floor equipment and assets installed in remote, hard-to-reach locations.
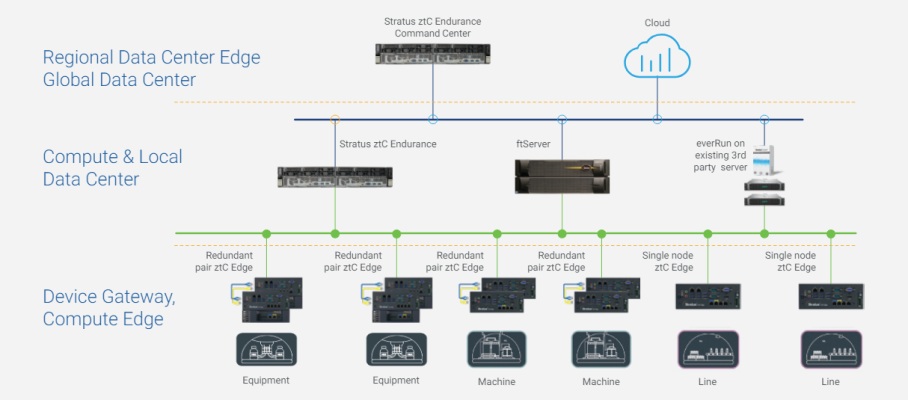
An Edge Computing platform collects critical data from sensors and equipment in a manufacturing environment, for example, and processes it in near real-time, empowering organizations to maximize operational efficiency, improve performance, and automate business processes, ensuring “always on” availability. Having compute resources at the edge also minimizes both data latency and security risks, as data is processed locally instead of being sent up to the cloud.
Demand for industrial Edge Computing platforms will grow significantly, driven by growth in demand for applications requiring on machine or on production line physical hardware with the necessary computing power for functionality, such as analytics and control.
Edge Computing offers opportunities for organizations to improve their business and production processes, especially with near real-time visibility into operations. Bringing computing resources close to the critical equipment where operational data is generated gives leaders the ability to improve decision-making based on operational performance.
Why Edge Computing for infrastructure & applications
Many organizations and company leaders across industries, including food & beverage, oil & gas, OEM machine builders, and smart & commercial building management, leverage Edge Computing platforms that are simple and easy to deploy, install, and manage, are protected from interruptions and threats, and are autonomous – delivering constant availability with extensive remote management provisions. These modern Edge Computing platforms offer highly automated, low-touch computing capability with built-in virtualization, redundancy, automated data protection, and application recovery. Along with the decreasing cost of IoT sensors, Edge Computing provides teams with a new approach to network architecture and data collection, one that was previously cost-prohibitive.

Edge Computing also offers IT and operations departments benefits that improve performance through operations visibility and reliability for mission-critical applications, especially as IT teams are increasingly being brought in to support the evolving demands of digital transformation in the OT space.
Forward-looking leaders and organizations should prioritize exploring the possibilities of Edge Computing and then begin with initial implementations to learn and scale. Additionally, it’s essential for companies to invest in reliable edge solutions to avoid unplanned downtime and data loss. Leaders in a range of industries have identified high-value opportunities around process control, asset performance management, and reliability by harvesting crucial data from the edge.
Now is the time to jump start your Edge Computing initiative, explore the possibilities, and avoid getting left behind.
Check out this Edge Computing 101 eBook for use cases, perspectives from industry experts, and trend data to answer fundamental questions that you may have about Edge Computing.
Next Steps
Want to learn more? Check out these resources: