Leverage Edge Computing platforms to rapidly modernize HMI/SCADA solutions and maximize reliability
Traditional HMI/SCADA architectures have existed for many years, providing users with the capability to operate plants and facilities since the advent of modern automation and control. Although this is all good, demands for better, faster, and cheaper solutions have increased amid a rapid move toward digital transformation. Here, sometimes good is not enough.
Let’s look at how organizations leverage Edge Computing platforms to rapidly modernize HMI/SCADA solutions and maximize reliability.
What is Edge Computing?
Gartner defines Edge Computing as part of a distributed computing topology where information processing is located close to the edge where things and people produce or consume that information.
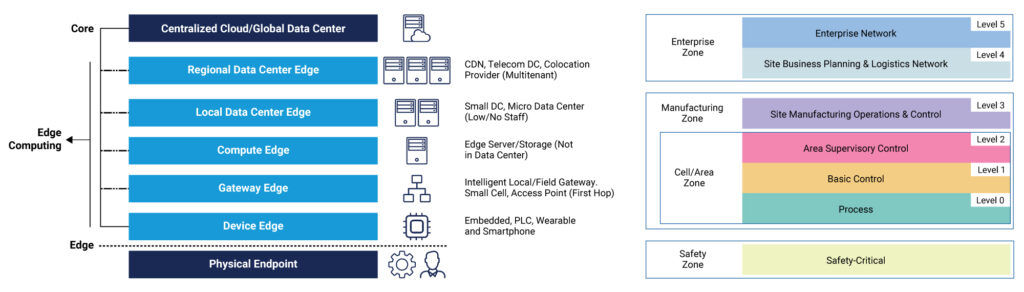
Gartner identifies multiple levels under Edge Computing.
- Device Edge – where you’ll find your PLCs, DCS, and other embedded control systems
- Gateway Edge – where you have the gateways that connect your controllers
- Compute Edge – this is composed of Edge servers and other plant floor monitoring and control devices
- The Local and Regional Data Center Edge – where you’ll find the micro data centers and control room equipment
- Centralized Cloud and Global Data Center – where you’ll find your command center and enterprise solutions
In essence, the Gartner Edge Computing topology is the edge version of the Purdue Model for industrial control systems. Combining the Gartner Edge topology with the Purdue Model provides us with a perfect view of the entire edge portfolio from device gateway and compute edge all the way up to enterprise.
The Gartner Topology vs The Purdue Model
Why is Edge Computing important?
For us to understand how to leverage the edge to rapidly modernize HMI and SCADA solutions and maximize reliability, let’s first talk about the top three challenges that engineers face when deploying or operating HMI and SCADA in their automation and control systems.
Challenge 1: Legacy systems and outdated manual processes
As more and more companies embark on digital transformation journeys, the demand for digitalization increases. With that being said, for organizations with legacy systems and old or manual processes in place, moving toward digital transformation can be a challenge. In automation and control, many customers are interested in connecting to more devices to get a better and more accurate reading turning that information into knowledge. The same customers want to integrate all edge solutions into the enterprise, and they want to be able to access that knowledge wherever they are in very different and useful formats.
Challenge 2: Disparate islands of automation
Over time, control systems age and expansion and upgrades add more nodes, leaving users with multiple computers for HMI/SCADA, Historian, MES, APM, advanced applications, and engineering i.e., disparate islands of automation. The result is multiple siloed nodes that are difficult to maintain and operate.
Challenge 3: Unplanned downtime
As any OT professional knows, unplanned downtime is unacceptable in a production environment. Unplanned downtime is very expensive, and in some cases may cause destruction of property.
How can you solve these challenges? The answer: Edge Computing
The switch is simple. Replace your traditional architecture’s existing computers and servers with a single, fault tolerant or high-availability Edge Computing platform.
Benefit from a no-compromise computing device
In the OT environment, you need a system that is easy to manage, reliable, and easily serviceable by OT teams.
The Stratus ztC Edge offers a no-compromise computing device designed to be deployed in an industrial environment, unlike commercial servers. It can operate in remote and hazardous environments and is Class I Division 2 Certified. It is a computing device that provides local control and monitoring at the machine and/or process area. Plus, you can install it in the same control panel as your UPS, DCS, PLCs, and other control equipment.
Take advantage of built-in virtualization
Stratus Edge Computing platforms come with both built-in virtualization and redundancy. This allows organizations to do more with less and to enable and accelerate automation. This is especially important if organizations install an HMI or SCADA device in a remote and/or hazardous location, with limited or no IT professionals to help set up and maintain your infrastructure. Built-in virtualization also allows you to consolidate multiple HMI and SCADA software together with other advanced software like Historian, MES, batch, asset performance, engineering, and programming into a single device — applications that would have otherwise been installed in multiple computers.
Enable cybersecurity at the edge
An Edge Computing Platform provides protection from outside attack, whether it be cyber or otherwise, as most come with built-in security capabilities like:
- Host-based firewall that lets you blacklist or whitelist IP addresses or domain names
- Restricted USB ports that help prevent the spread of malware
- Role-based access controls that authorize specific users and groups
- Secure communications protocols, and trusted boot that helps prevent cyber-attacks
Provide redundancy. Prevent downtime.
One of the best and simplest ways to provide a more reliable and modern HMI or SCADA system is to use an Edge Computing platform with built-in redundancy capabilities. Edge platforms with built-in redundancy have true high availability capabilities that prevent unplanned downtime from happening, as opposed to merely recovering from downtime. Plus, you avoid having to set up difficult-to-implement clustered solutions and save money by not having to buy additional software licenses.
The advantages of using Edge Computing platforms in HMI and SCADA solutions.
Workload consolidation
With Edge Computing, you can consolidate multiple physical assets into a single, more advanced, virtualized edge computer or server. Fewer devices deployed mean fewer devices to maintain and operate, less panel space and wiring required, and all your software assets are available in a single redundant and industrially hardened edge device. Plus, one single device makes it easier to implement solutions in industries that require GMP, validation, and regulation.
Operational resilience
Your software is only as good as the platform it runs on. Mission-critical applications need a platform that prevents unplanned downtime, provides redundancy, and is easy to implement. A ruggedized edge platform you can install in harsh environments (temperature, vibration, humidity, Class I Division 2), a platform you can install in a control panel together with the PLCs, drives, and other control equipment, and a platform that helps secure your control infrastructure from cyberattacks.
Want to learn more? Check out these resources.
Build Better HMI/SCADA Solutions with Edge Computing
Success at the Edge: 11 Customer Stories You Can Learn From
See how your company can benefit from Edge Computing